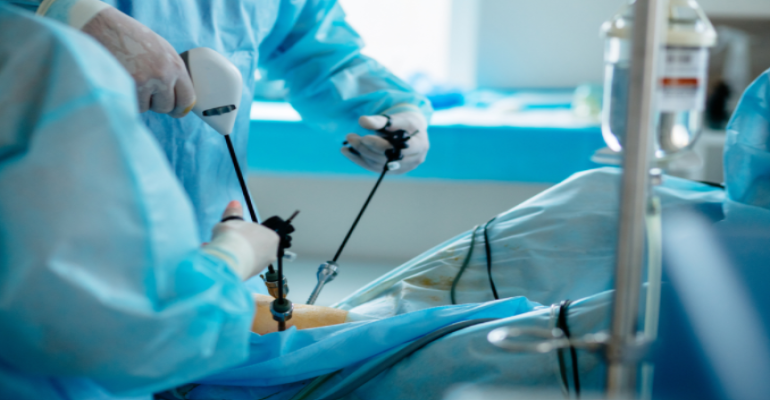
Thanks to groundbreaking advances in modern medicine, many surgical operations are now performed without large incisions. Laparoscopy, being at the forefront, causes fewer complications and maintains the patient's comfort at the highest level with a faster recovery time.
This method, used both for treatment and diagnosis, is commonly known as a closed surgery among the public.
What is laparoscopy?
It is a minimally invasive surgical approach performed through small incisions made in the abdominal area. This surgical technique, performed using devices called laparoscopes, allows access to the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
A laparoscope is a thin, illuminated tube with a high-resolution camera at its tip, which enables visualization of the abdominal cavity and pelvis on a monitor. The surgeon performs necessary procedures by viewing these images on the monitor.
Normally, in open surgeries, the incision is quite large to obtain a visual field, whereas in laparoscopy, the incision size ranges between 1 to 1.5 cm.
Why is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopy, frequently preferred in gynecology today, can be used for diagnosis and treatment of many diseases occurring inside the abdomen and pelvis. Accordingly;
- Removal of cysts and myomas
- Termination of ectopic pregnancy
- Removal of a damaged organ
- Removal of the uterus
- Taking tissue samples
- This procedure can be comfortably applied in the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, and all female reproductive system diseases.
- Cancer surgeries
Most pelvic diseases can be diagnosed with imaging methods such as ultrasound, computed tomography, or MRI. However, in some cases, laparoscopy must be performed to make a definitive diagnosis.
At this point;
- Infertility
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Ovarian cysts
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Fibroids
- Ovarian cancers can also be evaluated with this method.
How is laparoscopy performed?
This procedure is a closed operation performed under general anesthesia. The patient should not eat or drink for about 12 hours before the surgery and should not use blood thinners.
Such conditions must be reported to the doctor. The duration of the procedure varies depending on the disease being treated. A needle is inserted through the patient's navel to inflate the abdominal cavity with CO2 (carbon dioxide). Then a camera is inserted into the abdomen to illuminate the interior and provide a clearer view of all organs.
If necessary, additional small incisions are made in different areas of the abdomen to insert auxiliary instruments. The laparoscopic surgery is completed after performing the required procedures. Being a bloodless, scalpel-free, and comfortable application, there is no need for worry or surgery-related stress.
What should be considered after laparoscopy?
The carbon dioxide given into the abdomen during surgery may cause shoulder pain when the patient stands up, but this is completely temporary. Hidden stitches are used in the surgery and these stitches dissolve on their own.
Therefore, the patient does not need to perform any care for the stitches. Showering is allowed within 48 hours after surgery, but the surgery site and nearby areas must not be scrubbed.